AIDEA is an AI-driven platform designed to enhance communication with AI. It offers features like saving prompts, customizing prompts, and building personalized prompts using AIDEA's SPARK custom GPT. This tool aims to streamline AI interactions, automate tasks, and improve overall efficiency for users engaging with artificial intelligence.
AIDEA
Interfacing with AI
This document explores the various ways humans interact with artificial intelligence (AI).
Types of Interfaces
* Text-based Interfaces: These interfaces allow users to communicate with AI systems through written language.
* Examples include chatbots, command-line interfaces, and search engines.
* Voice-based Interfaces: Users interact with AI using spoken words.
* Examples include virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
* Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs): These interfaces use visual elements like icons, buttons, and menus to enable interaction with AI.
* Examples include AI-powered image editing software and virtual reality experiences.
* Gesture-based Interfaces: Users control AI systems through physical movements.
* Examples include motion-controlled gaming and sign language recognition.
Challenges of AI Interfacing
* Natural Language Understanding (NLU): AI systems struggle to fully understand the nuances of human language.
* Contextual Awareness: AI often lacks the ability to understand the broader context of a conversation or interaction.
* Personalization: Creating AI interfaces that are tailored to individual user preferences and needs can be complex.
* Ethical Considerations:
* Bias in AI algorithms can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
* Privacy concerns arise when AI systems collect and process personal data.
Future of AI Interfacing
* More Natural and Intuitive Interactions: Advancements in NLU and machine learning will lead to AI systems that can understand and respond to human input more naturally.
* Multi-modal Interfaces: Future interfaces will likely combine multiple input methods (e.g., text, voice, gesture) for a richer and more immersive experience.
* Personalized AI Assistants: AI assistants will become increasingly personalized, anticipating user needs and providing customized support.
* Ethical AI Development:
* Researchers and developers will continue to work on mitigating bias and ensuring responsible use of AI.
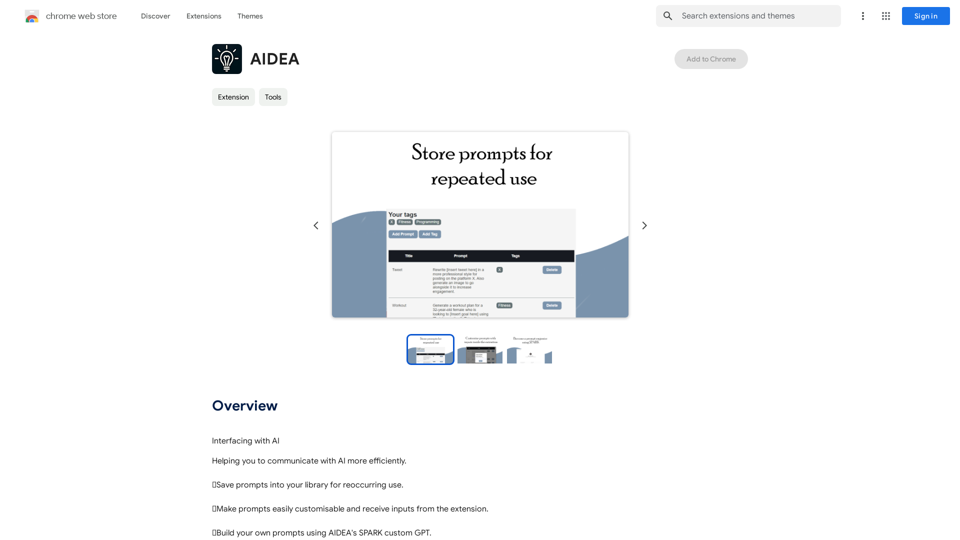
Introduction
Feature
Save Prompts to Your Library
Users can save frequently used prompts into their personal library for quick and easy access, facilitating efficient reuse for recurring tasks.
Customizable Prompts
AIDEA allows users to easily customize prompts and receive inputs directly from the extension, enabling more tailored and effective AI interactions.
Build Your Own Prompts with SPARK
Utilizing AIDEA's SPARK custom GPT, users can create their own unique prompts, offering a high level of personalization and flexibility in AI communication.
Task Automation
AIDEA simplifies task automation, helping users save valuable time and increase productivity in their AI-related workflows.
Flexible Usage Options
While all users can access core features, a subscription model offers extended benefits and usage limits beyond the free tier.
FAQ
What is AIDEA?
AIDEA is an AI-driven platform that enhances communication with AI by providing features like prompt saving, customization, and creation using SPARK custom GPT.
What are the main features of AIDEA?
The main features include saving prompts to a personal library, customizing prompts, building unique prompts with SPARK custom GPT, and task automation.
How do I use AIDEA?
Users can access AIDEA's features such as saving prompts, customizing them, and creating new ones. Subscribing unlocks additional benefits and extended usage limits.
What are the benefits of using AIDEA?
Key benefits include time savings through task automation, improved AI interactions via customized prompts, and the ability to create personalized prompts using SPARK custom GPT.
How much does AIDEA cost?
AIDEA offers various pricing plans, including a free tier and paid options with additional features and benefits.
Related Websites
Here is the translation: AI Photo, Photo AI, AI Photo Editing, AI Generated Photos, Free AI Photo Editor, AI Photo Generator, AI Avatar Generator
105
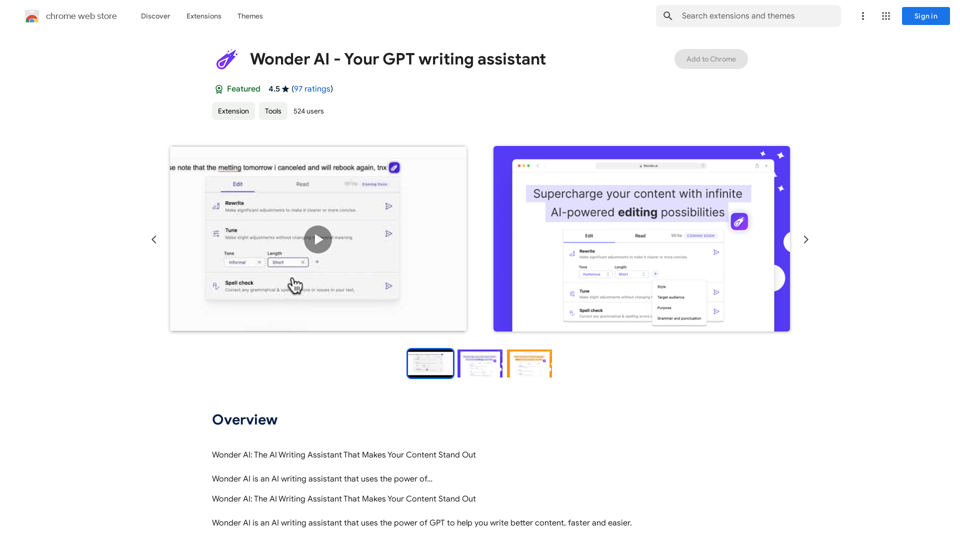
Wonder AI: The AI Writing Assistant That Makes Your Content Stand Out Wonder AI is an AI writing assistant that uses the power of artificial intelligence to help you create high-quality, engaging content that resonates with your audience.
193.90 M
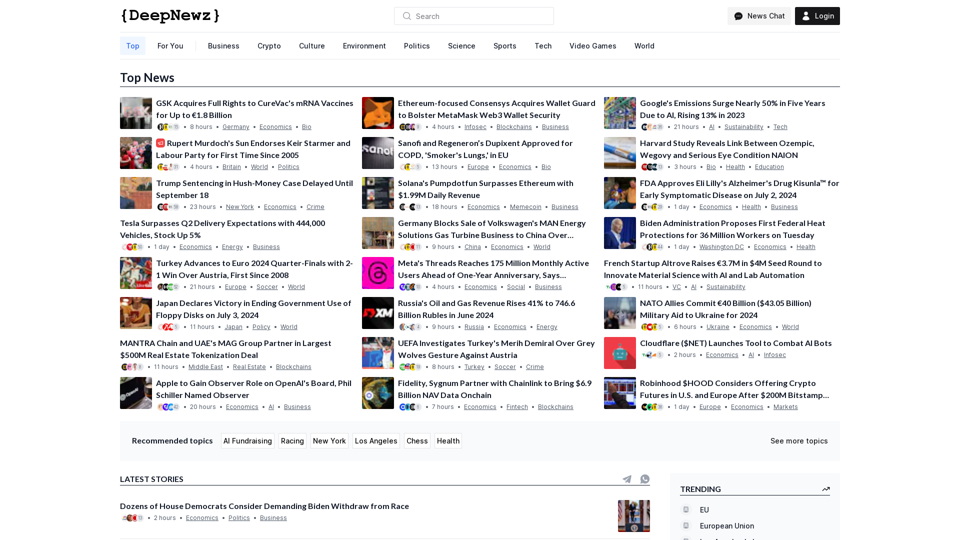
Find the latest top stories spanning all industries, from technology giants like OpenAI and Nvidia to pop culture updates featuring Taylor Swift and Ice Spice, alongside coverage of political figures like Joe Biden and Donald Trump and economic insights on major companies such as Facebook, Apple, and Google.
38.98 K
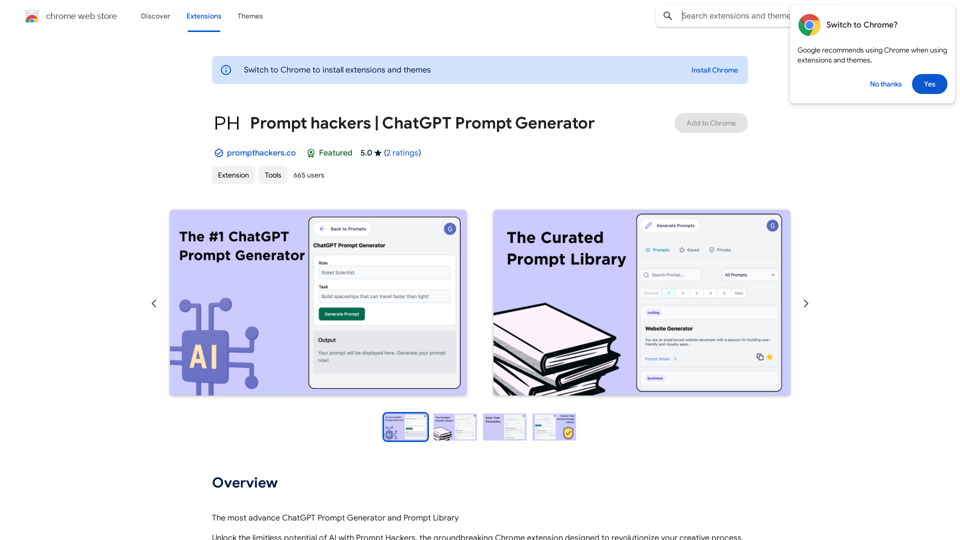
Prompt Hackers ===================== Generate creative and effective prompts to get the most out of your language model.
Prompt Hackers ===================== Generate creative and effective prompts to get the most out of your language model.The Most Advanced ChatGPT Prompt Generator and Prompt Library
193.90 M